Maintaining good posture isn’t just about looking confident, it plays a vital role in protecting your bones and overall musculoskeletal health. The way you sit, stand, and even hold your head directly impacts the alignment of your spine and the strength of your supporting muscles. Poor posture over time can place excess stress on the bones, joints, and ligaments, leading to discomfort, mobility issues, and in some cases, long-term damage.
From hunching over your phone to sitting for hours at a desk, modern lifestyles often encourage positions that silently strain the body. Recognising these postures and their potential risks is the first step in preventing bone-related problems and maintaining a healthier, pain-free future.
ALSO READ: When Endometriosis Turns Deadly: Understanding Its Link To Ovarian Cancer
Kyphotic Posture
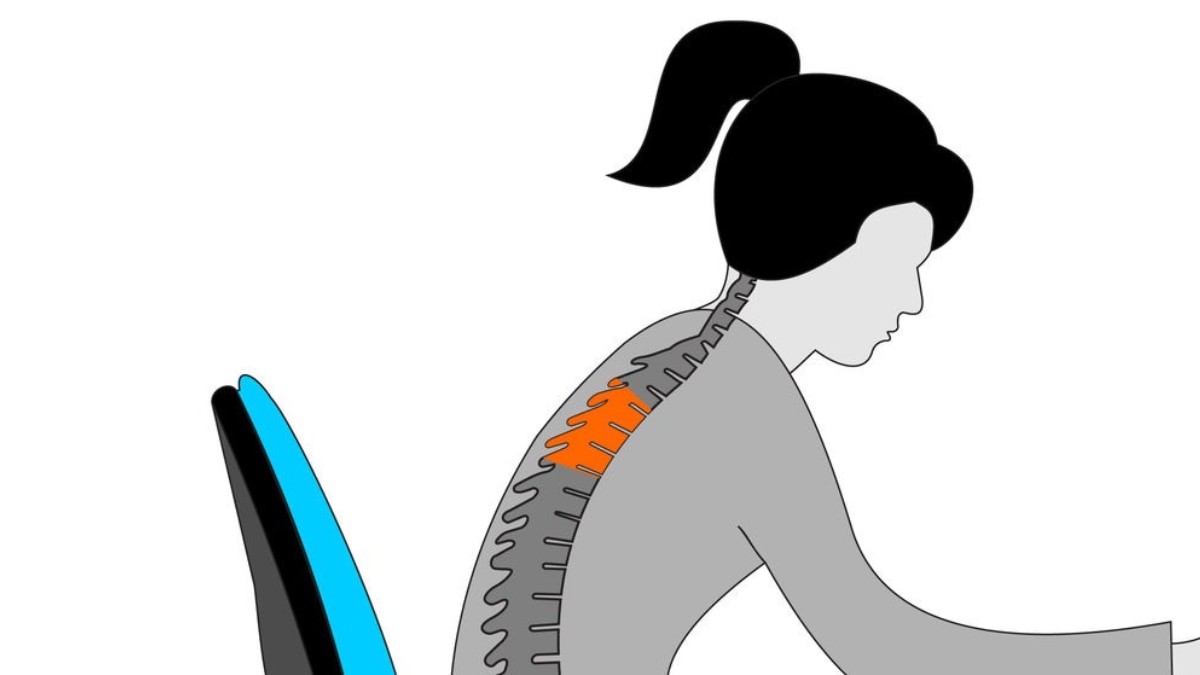
Often referred to as a ‘hunchback,’ this posture involves excessive rounding of the upper back. It compresses the chest, makes breathing harder, and is frequently seen in office workers, taller individuals, and people constantly hunched over devices.
Lordosis
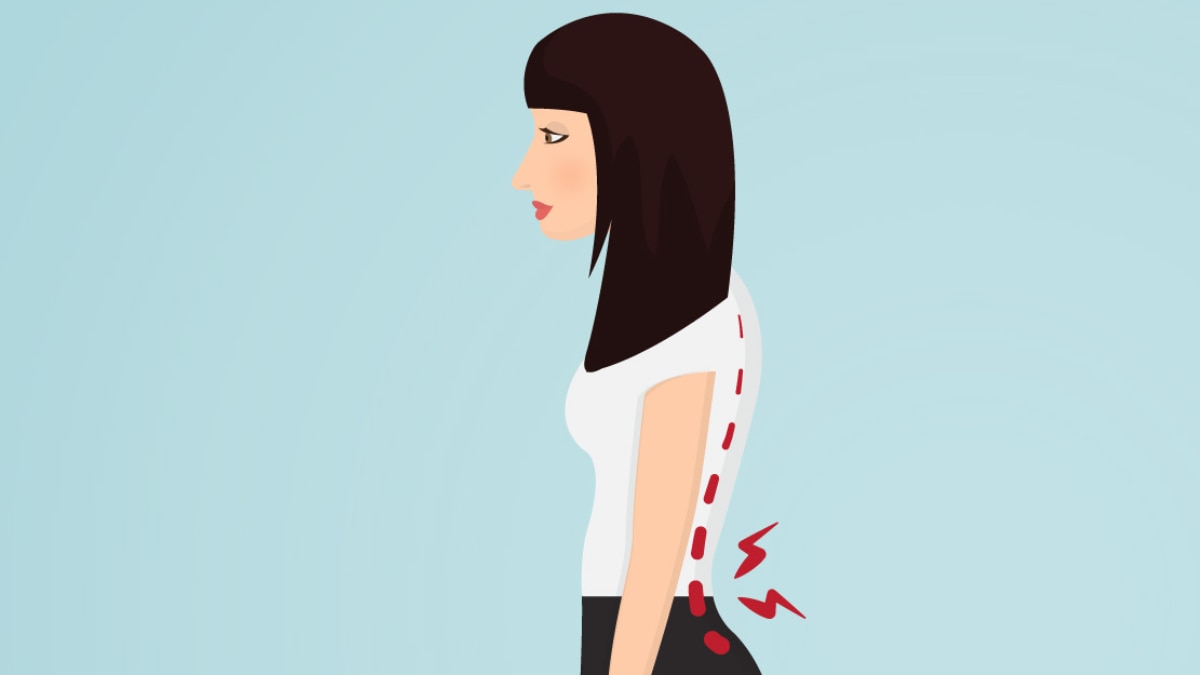

Known as ‘swayback,’ lordosis is marked by an exaggerated inward curve of the lower back. It can tilt the pelvis forward, push the stomach and buttocks outward, and strain the lower back muscles. Pregnant women, truck drivers, and people wearing high heels often experience this posture.
Flat Back Posture
In this posture, the natural lumbar curve is reduced or absent. People often lean forward and struggle to stand upright for long periods. Flat back posture can occur due to compression fractures or degenerating discs.
Forward Head
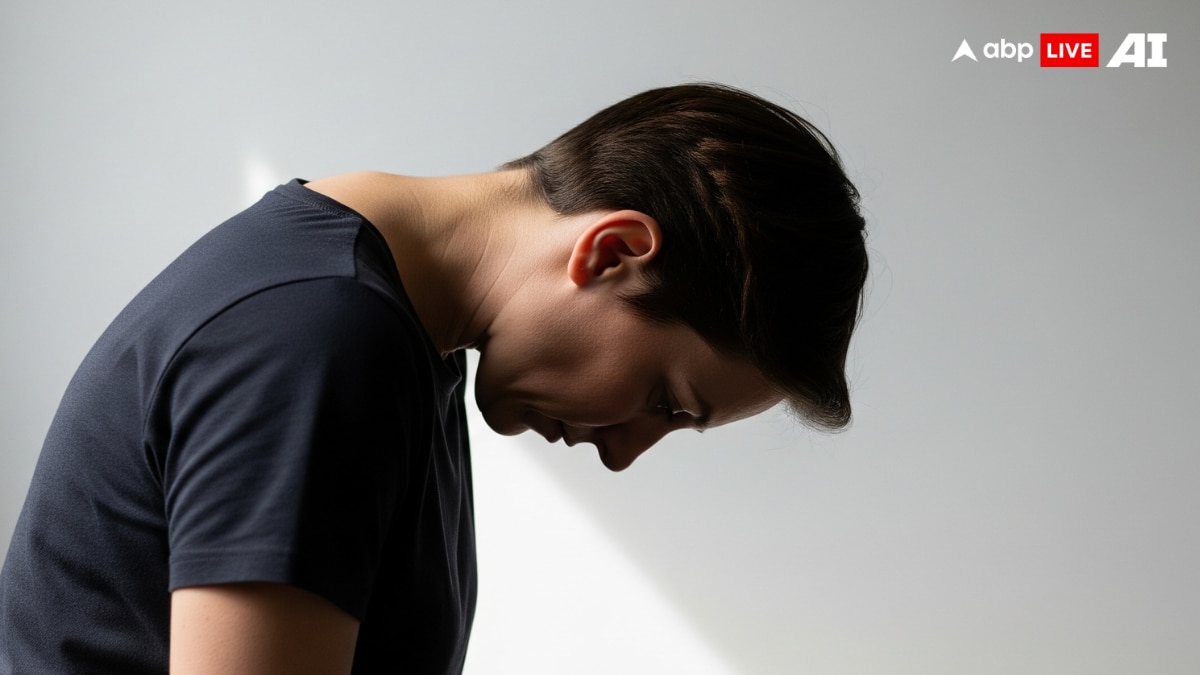

Popularly called ‘tech neck,’ this posture happens when the head juts forward beyond the shoulders. It often leads to neck stiffness, headaches, and shoulder pain. Spending long hours on computers, mobile devices, or carrying heavy backpacks are common causes.
[Disclaimer: The information provided in the article is intended for general informational purposes only. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.]
Check out below Health Tools-
Calculate Your Body Mass Index ( BMI )
Calculate The Age Through Age Calculator

